Types of Robotic Arms in Industrial Automation
Robotic arms have become a foundational component in modern industrial automation. From enhancing precision and productivity to ensuring consistent quality and operational safety, robotic arms are central to the transformation of traditional manufacturing and assembly lines. As production demands shift toward higher flexibility and reduced human intervention, robotic systems are increasingly seen as indispensable assets in diverse sectors such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
Kingstone Robotics, as a comprehensive automation integrator, collaborates with world-renowned industrial robotics manufacturers such as FANUC, KUKA, ABB, Universal Robots, and others. Through these strategic partnerships, Kingstone offers customers a wide selection of robotic arms, optimized for the specific demands of different applications. These integrations enable industries to not only adopt automation but to adapt it efficiently into their existing workflows.
Types of Robotic Arms and Their Characteristics
1. Articulated Robot Arm
Overview
An articulated robot arm is modeled after the human arm, featuring 4 to 6 rotary joints (axes). Each joint provides an individual degree of freedom, allowing for multi-directional motion and exceptional flexibility in three-dimensional space. This makes articulated arms ideal for tasks requiring high maneuverability and precision.
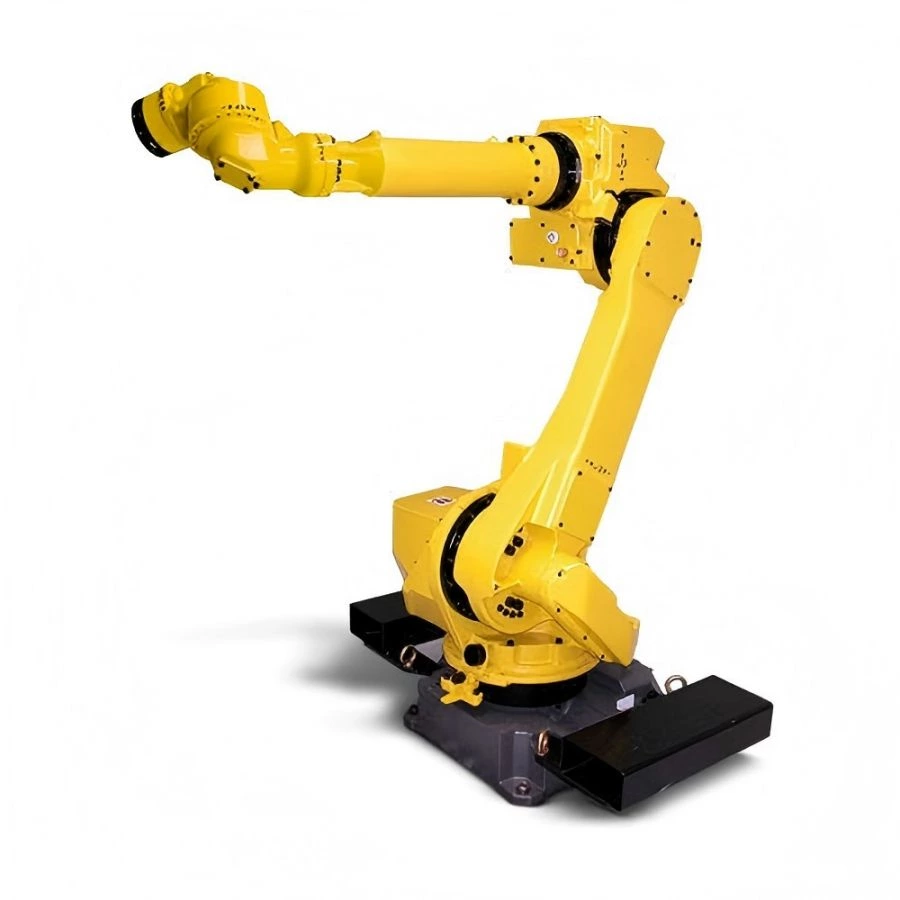

Specifications & Application Overview
| Feature | Description / Application |
| Joint Type | Rotary (4–6 axes) |
| Degrees of Freedom | High – supports complex, multi-angle motion |
| Work Envelope | 3D – suitable for confined, irregular, or multi-surface environments |
| Precision | High repeatability – ideal for tasks requiring accuracy and consistency |
| Welding | Arc welding, spot welding in automotive and metal fabrication |
| Finishing | Surface treatment such as grinding, sanding, polishing, and painting |
| Assembly | Automated component assembly, especially in electronics or machinery sectors |
| Material Handling | Loading/unloading, part transfer, machine tending |
| Logistics / Packaging | Palletizing, boxing, and order fulfillment in warehouses |
Advantages
- Highly flexible: Ideal for operating in complex or tight spaces
- Wide range of motion: Capable of following intricate paths
- Versatile use: Suitable for both high-speed and high-precision operations
Representative Models
| Brand | Model | Notable Features |
| FANUC | M-20iA | Six-axis; excellent for assembly and material handling |
| KUKA | KR AGILUS | High speed and precision in compact environments |
| ABB | IRB 2600 | Small footprint, high versatility, strong repeatability |
Kingstone Recommendation
Articulated arms are best suited for robotic polishing and deburring stations, especially for complex 3D components such as:
Their multi-axis flexibility allows for accurate surface tracking, making them highly effective in high-precision finishing workflows.
2. SCARA Robot (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot) Arm
Overview
SCARA robots are designed for fast, precise horizontal movements with a rigid vertical axis, making them ideal for planar assembly tasks. The name “Selective Compliance” refers to their flexibility in the X-Y plane and rigidity in the Z-axis, allowing controlled compliance where needed and stiffness where precision is essential.
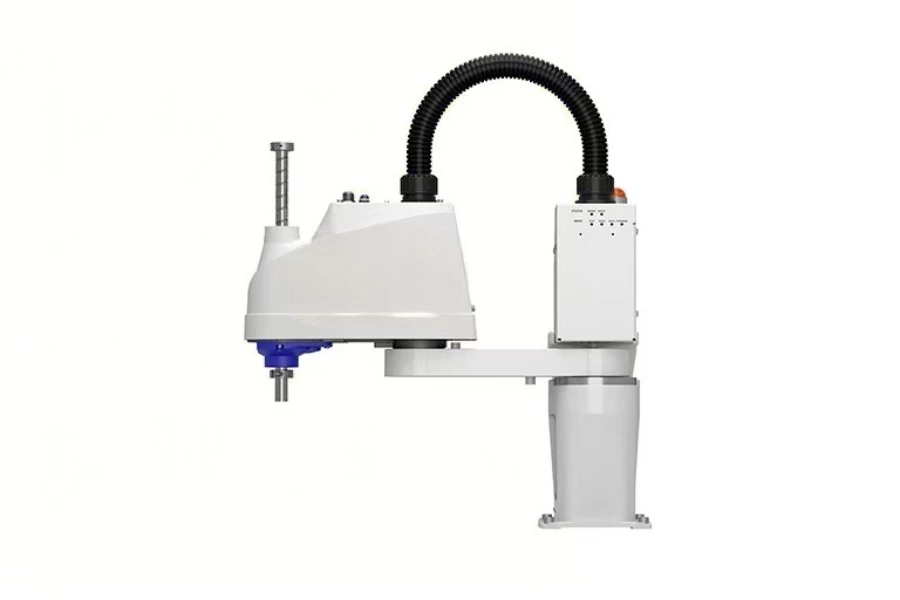

Specifications & Application Overview
| Feature | Description / Application |
| Joint Configuration | Two rotary joints (for X-Y motion) and one vertical axis (Z motion) |
| Degrees of Compliance | Compliant in horizontal plane; rigid in vertical direction |
| Speed | High – ideal for rapid pick-and-place and insertion tasks |
| Precision | Excellent repeatability for fine, repetitive operations |
| Assembly | High-speed component insertion, screw fastening, or plug-in PCBA assembly |
| Material Handling | Pick-and-place of small or lightweight components |
| Dispensing Tasks | Suitable for fluid dispensing in electronics or medical device manufacturing |
| Packaging | High-throughput packing in pharmaceutical or electronics industries |
Advantages
- Fast horizontal motion, ideal for repetitive, high-speed production lines
- High accuracy and consistency, even during continuous operation
- Compact footprint, suitable for dense workstations or tabletop environments
Representative Models
| Brand | Model / Series | Key Features |
| Epson | SCARA Robot Series | Known for precise motion and integration flexibility |
| Yamaha | YK-X Series | Offers a range of stroke options with high-speed and low-vibration |
| Omron Adept | SCARA Robots | Compact, reliable, and easily programmable for factory automation |
Kingstone Recommendation
SCARA robots are ideal for high-speed precision assembly lines, especially in the production of medical device pre-assemblies, 3C electronic components, or PCBA insertion tasks. Their fast cycle times, precision, and compact structure make them a top choice for automated micro-assembly stations where speed and footprint matter.
3. Cartesian Robot Arm
Overview
Cartesian robots, also known as rectilinear or gantry robots, move along three orthogonal linear axes (X, Y, Z). These systems follow a rectangular coordinate framework, enabling pure translational motion without rotation. This structure allows for high precision, simplicity in programming, and ease of scalability for large or customized work areas.
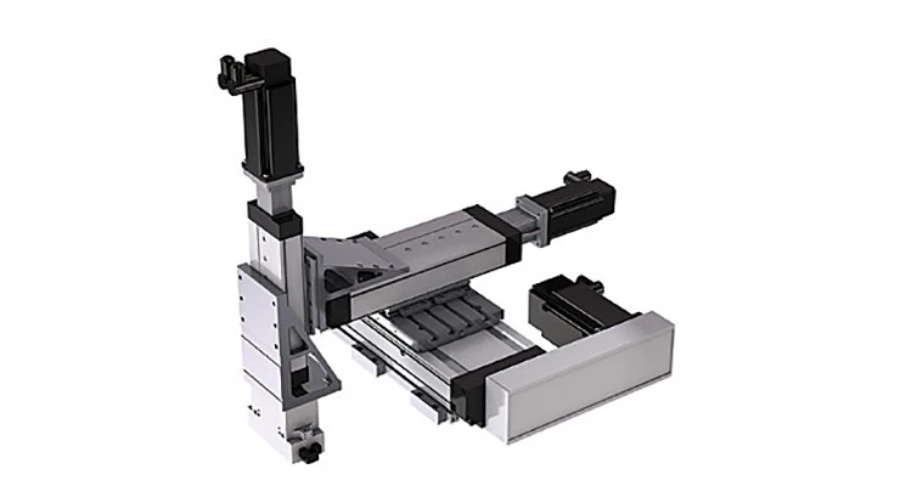
Specifications & Application Overview
| Feature | Description / Application |
| Motion Type | Linear motion along X, Y, and Z axes |
| Degrees of Freedom | 3 – All translational; no rotary joints |
| Programming Complexity | Low – movement follows Cartesian coordinates, simplifying path planning |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large-format applications or extended reach |
| Accuracy | Excellent for precise point-to-point positioning |
| Material Handling | Used in sheet metal loading, heavy object transfer, or rail-mounted automation |
| Laser Processing | Applied in laser cutting, trimming, or engraving on large or curved surfaces |
| Additive Manufacturing | Core mechanism for 3D printing systems |
| Labeling & Inspection | For accurate, repeatable motion in large work envelopes |
Advantages
- Simple structure with easy maintenance
- High precision and repeatability for point-to-point tasks
- Easily customizable stroke lengths for extended workspaces
- Ideal for multi-machine coordination in large factories
Representative Models
| Brand | Model / Series | Key Features |
| IAI | Cartesian Robots | Modular, actuator-based systems with high flexibility |
| Bosch Rexroth | Cartesian Motion Systems | Robust industrial solutions for heavy-duty and precision tasks |
| HIWIN (Taiwan) | Linear Robot Series | Known for scalability and integration with large-format applications |
Kingstone Recommendation
Cartesian robots are best suited for material loading across multiple stations, rail-mounted automation, and precise coordination in multi-machine environments. Their structured linear motion and expandable work envelope make them ideal for tasks such as:
- Sheet metal handling
- Laser trimming of curved or oversized surfaces
- Pallet transfer or part sorting over long distances
They are a top choice where repeatability, scalability, and ease of integration are critical.
4. Delta Robot (Parallel-Link Robot) Arm
Overview
Delta robots use three lightweight arms connected in a triangular parallel configuration, mounted to a fixed base. These arms control a central end-effector suspended below, allowing for ultra-fast and precise motion within a dome-shaped work envelope. Their low moving mass and parallel mechanics make them ideal for high-speed, pick-and-place applications.
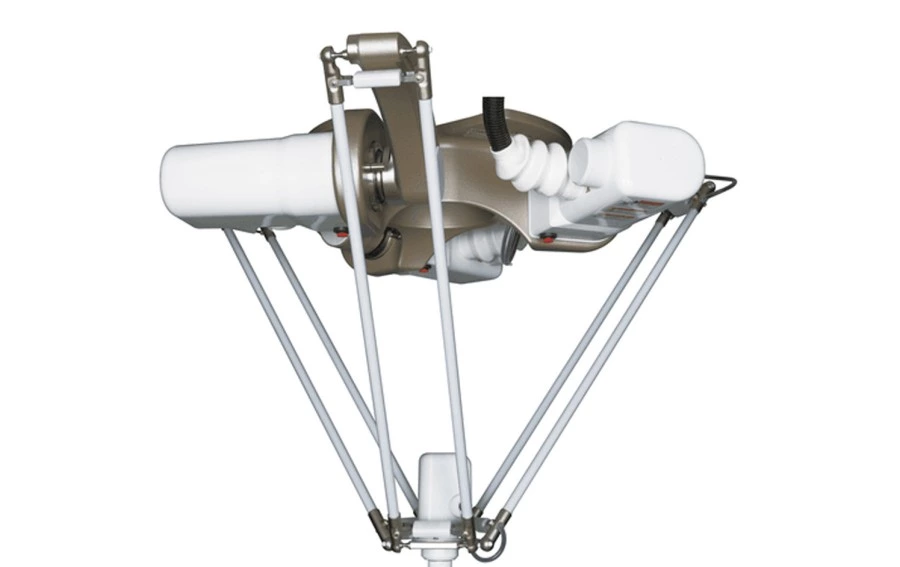

Specifications & Application Overview
| Feature | Description / Application |
| Kinematic Structure | Parallel mechanism with three arms and a central end-effector |
| Work Envelope | Dome-shaped, ideal for shallow and wide-area tasks |
| Speed | Extremely high – optimized for rapid pick-and-place operations |
| Payload | Light – ideal for small parts or lightweight packaging tasks |
| Precision | High – suitable for micro-component handling and delicate manipulation |
| Packaging | High-speed sorting and boxing in food, pharma, and cosmetics industries |
| Electronics Handling | Ideal for tiny component placement or inspection in PCB assembly lines |
| Pharmaceuticals | Applied in vial sorting, capping, and lab automation |
Advantages
- Exceptionally fast cycle times, outperforming other robot types in speed
- Low moving mass, enabling high acceleration and minimal vibration
- Compact footprint, allowing easy integration into tight or modular production cells
- Ideal for high-throughput, lightweight automation tasks
Representative Models
| Brand | Model / Series | Key Features |
| ABB | FlexPicker | Industry leader in high-speed food and packaging automation |
| FANUC | M-1iA Delta Robot | Compact design, vision-enabled, ideal for electronics and small parts |
| Omron | Delta Series | Flexible for pharmaceuticals, electronics, and fast sorting lines |
Kingstone Recommendation
Delta robots are highly recommended for smart packaging lines, pharmaceutical sorting, and 3C electronics part handling, where speed and responsiveness are critical. Ideal for:
- Sorting and boxing in food and consumer goods
- High-speed vial capping in pharmaceutical production
- Rapid placement of micro-components in electronic assembly
Their parallel design enables unmatched speed with high precision, making them essential for modern high-throughput production lines.
5. Cylindrical Robot Arm
Overview
Cylindrical robots operate within a cylindrical coordinate system, combining rotary base motion, vertical column movement, and radial linear extension. This configuration enables controlled access to vertical and outward positions, making it ideal for tasks that require vertical reach and radial precision within a compact footprint.
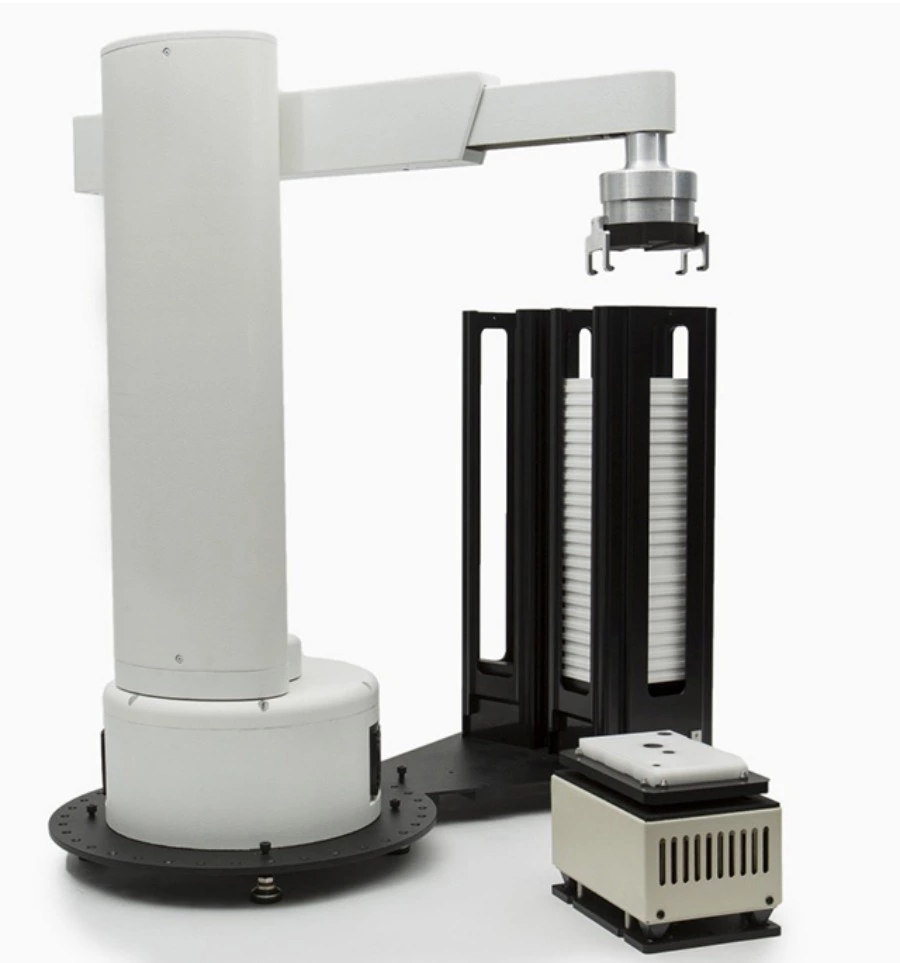

Specifications & Application Overview
| Feature | Description / Application |
| Kinematic Structure | Rotary base + vertical column + horizontal linear arm |
| Work Envelope | Cylindrical – suitable for operations around a central vertical axis |
| Reach Characteristics | Good vertical stroke with radial extension and 360° base rotation |
| Footprint | Compact – optimized for installations where space efficiency is a priority |
| Machine Tending | Ideal for loading/unloading injection molding machines, lathes, or CNC centers |
| Welding | Suitable for arc welding tasks that require consistent reach around a fixed point |
| Part Transfer | Effective in assembly line transport and mid-range component handling |
Advantages
- Efficient use of vertical space in tight production areas
- Simple and compact mechanical structure
- Rotary access to surrounding stations without large horizontal movement
- Well-suited for vertical integration with machinery
Representative Models
| Brand | Model / Series | Key Features |
| Mitsubishi Electric | Cylindrical Robot Line | Compact solutions for machine loading and simple transfer tasks |
| Nachi-Fujikoshi | Cylindrical Series | Focused on stability, reach, and integration with machining lines |
Kingstone Recommendation
Cylindrical robots are optimized for midsize vertical machine tending applications, especially in tight production cells or machines arranged in radial layouts. Recommended use cases include:
- Surrounding injection molding machines
- Feeding CNC lathes or vertical machining centers
Their compact, vertically oriented structure makes them ideal for space-constrained work environments where radial reach is essential.
6. Polar Robot (Spherical Coordinate Robot ) Arm
Overview
Polar robots—also known as spherical coordinate robots—combine two rotary joints and one telescopic linear joint, allowing the arm to operate within a spherical work envelope. This structure provides a wide radial reach while maintaining a mechanically simple design, making it well-suited for tasks requiring broad coverage around a central axis.
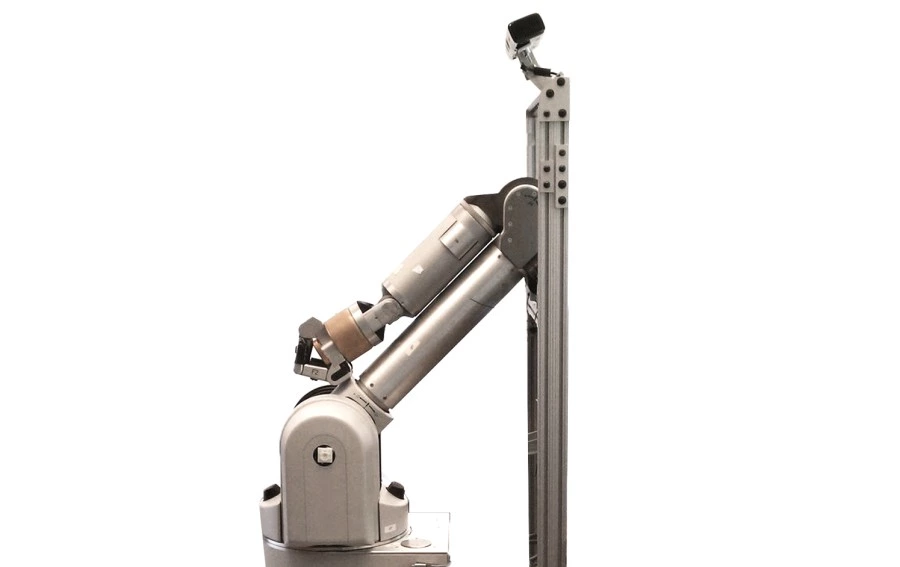

Specifications & Application Overview
| Feature | Description / Application |
| Kinematic Structure | Base rotation + shoulder pivot + telescopic arm (radial extension) |
| Work Envelope | Spherical – optimized for large-radius, sweeping motions |
| Degrees of Freedom | Typically 3 – two rotary, one linear |
| Mechanical Complexity | Low – fewer components mean reduced maintenance needs |
| Painting & Coating | Ideal for automotive body painting, spray coating, or surface treatment |
| Foundry Operations | Effective for post-casting retrieval, hot part handling, or core removal |
| Bulk Handling | Suitable for material bin sorting and large object reorientation |
Advantages
- Large radial reach for wide-area operations
- Simple mechanical structure reduces maintenance complexity
- Easily integrates into peripheral stations arranged in circular or semi-circular layouts
- Suitable for heavy-duty or thermally challenging environments
Representative Models
| Brand | Model / Series | Key Features |
| Stäubli | TX Series (comparable) | Though not a pure polar model, it uses similar kinematics for wide-range painting and handling |
Kingstone Recommendation
Polar robots are ideal for large-radius industrial operations where the task requires both extended reach and stationary base positioning. They are especially efficient in:
- Automotive painting lines
- Post-heat-treatment frame sorting
- Foundry bin loading/unloading or heavy part repositioning
Their spherical workspace and long radial extension make them suitable for centralized installations covering broad perimeters with minimal footprint.
7. Collaborative Robot (Cobot) Arm
Overview
Collaborative robots—commonly known as cobots—are designed to work safely alongside humans without traditional safety cages. They incorporate force sensing, collision detection, and compliance control to enable safe, responsive, and adaptive movement. Cobots are ideal for tasks requiring human-robot interaction, light-duty automation, and frequent reconfiguration.
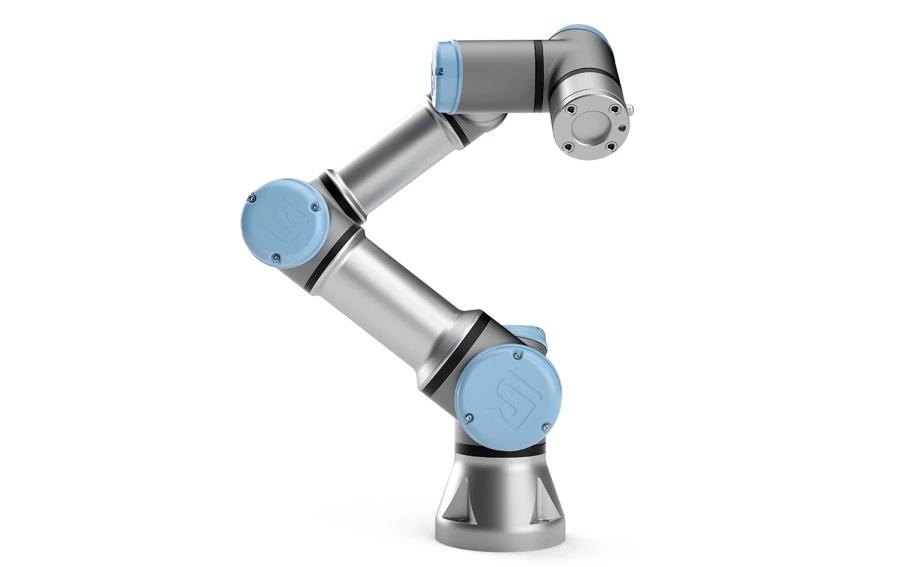
Specifications & Application Overview
| Feature | Description / Application |
| Safety Features | Built-in force feedback, collision detection, and power/force limiting |
| Programming | Intuitive interface, often drag-and-drop or hand-guiding |
| Deployment | Rapid setup and easy relocation between workstations |
| Assembly Tasks | Ideal for light component fitting, flexible production cells |
| Testing & Inspection | Used in sensor-based checking, button actuation, or gauging |
| Surface Finishing | Enables light-duty polishing, brushing, or deburring with consistent pressure |
| Human-Robot Interaction | Supports shared workspaces and multi-process collaborative environments |
Advantages
- Safe for direct interaction without cages or barriers
- Quick to program and redeploy, reducing downtime between tasks
- Compact and lightweight, suitable for desktop or mobile platforms
- Ideal for low-volume, high-mix production environments
Representative Models
| Brand | Model / Series | Key Features |
| Universal Robots | UR3 / UR5 / UR10 / UR20 | Industry-standard cobots with high adaptability and payload versatility |
| Doosan Robotics | A, H, M, E Series | Strong safety features, torque sensing, and user-friendly interfaces |
| Techman Robot (TM) | TM5 / TM12 / TM14 Series | Integrated vision system and intuitive graphical programming |
Kingstone Recommendation
Cobots are ideally suited for integration with Kingstone’s in-house polishing modules, especially for precision surface finishing tasks that benefit from tactile force feedback. Typical applications include:
- Polishing stainless steel medical device enclosures
- Flexible multi-process stations where human and robot alternate or share tasks
- Desktop-level polishing or testing cells in small-batch manufacturing
Their ease of deployment, compact size, and safety-certified control systems make them a natural choice for modern collaborative automation scenarios.
Applications of Robotic Arms in Industrial Automation
Robotic arms are a cornerstone of industrial automation, valued for their precision, consistency, and flexibility across manufacturing sectors. Their deployment enhances efficiency, minimizes human error, and supports high-throughput, scalable operations.
- Assembly
Widely used in electronics and automotive production, robotic arms handle small, delicate components with micron-level precision, enabling fast, uninterrupted assembly lines. - Material Handling
Robotic arms streamline loading, unloading, part transfer, and palletizing, improving internal logistics and reducing the physical strain on workers in multi-process environments. - Welding
Articulated robots ensure consistent weld quality and precise joint penetration, especially in automotive body and chassis manufacturing, while enhancing workplace safety by limiting human exposure to heat and fumes. - Painting
Automated spray systems provide uniform coverage and precise material control, reducing overspray and ensuring high-quality finishes in industries such as automotive and appliance manufacturing. - Polishing and Grinding
In metal finishing, robots deliver stable pressure and repeatable motion—ideal for complex 3D surfaces in parts like aerospace components, medical enclosures, and automotive housings.
Factors in Robotic Arm Selection
Choosing the right robotic arm is essential for performance, efficiency, and return on investment—especially when integrating with Kingstone’s polishing, deburring, or handling systems.
- Degrees of Freedom & Work Envelope: Select based on part geometry and motion requirements. Complex 3D paths may require 6-axis arms, while planar tasks suit SCARAs or Cartesian robots.
- Payload & End Effector: Ensure the robot supports the weight of Kingstone’s custom tools (e.g., polishing heads). Undersized payloads reduce accuracy and tool life.
- Repeatability: For sub-millimeter tasks, use high-precision models from ABB, FANUC, or KUKA.
- Human Collaboration: For shared workspaces, cobots like Universal Robots (UR) offer safe, flexible interaction.
- ROI Considerations: Balance robot cost with expected cycle time, labor savings, and process efficiency.
- Space & Installation: Use compact SCARAs or tabletop cobots in tight areas. For extended reach, consider track-mounted articulated arms.
Proper selection ensures reliable, long-term performance within Kingstone’s automation solutions.
Kingstone Robotics’ Integration Advantages
Kingstone Robotics offers comprehensive robotic integration solutions tailored to high-precision manufacturing industries. Our strength lies in combining world-class robotic platforms with deep process expertise.
1. Multi-Brand Integration
We integrate leading industrial robots from top global brands, including ABB, FANUC, KUKA, YASKAWA, and Universal Robots (UR)—ensuring optimal performance for every application.
2. Industry-Specific Customization
Solutions are engineered to meet the unique demands of each sector:
- Automotive: Transmission housing and steering knuckle polishing
- Aerospace: Turbine disk deburring and fan blade finishing
- Medical: Polishing of stainless steel and titanium alloy casings
3. End-to-End Delivery
Kingstone provides full project lifecycle support:
- Feasibility studies and simulation
- Custom tooling and fixture design
- Complete automation line deployment
- Reliable after-sales service and technical support
By combining flexible robotic platforms with domain-specific know-how, Kingstone delivers efficient, scalable, and high-precision automation systems.
Conclusion
Robotic arms are fundamental to modern manufacturing, offering unmatched versatility across industries. Their wide range of configurations—from articulated and SCARA to delta and collaborative robots—enables them to meet the demands of processes as diverse as heavy-duty machining and high-precision cleanroom assem
bly.
However, effective implementation requires more than just hardware. Choosing the right robotic system demands a clear understanding of process requirements, part geometries, and production objectives.
By partnering with Kingstone Robotics, manufacturers gain more than access to world-class robots—they benefit from expert integration, customized tooling, and application-specific automation strategies. This ensures not only optimal performance and flexibility, but also scalability and measurable return on investment.
Kingstone transforms robotic automation from a technical upgrade into a long-term productivity advantage.
References
- FANUC Robotics – https://www.fanucamerica.com
- KUKA Robotics – https://www.kuka.com
- ABB Robotics – https://new.abb.com/products/robotics
- Universal Robots – https://www.universal-robots.com
- Epson SCARA Robots – https://epson.com/For-Work/Robots/scara
- Mitsubishi Electric Robotics – https://us.mitsubishielectric.com/fa/en/products/robots
- Omron Adept Technology – https://industrial.omron.com
- HIWIN Technologies – https://www.hiwin.tw
- IAI Corporation – https://www.intelligentactuator.com
- Staubli Robotics – https://www.staubli.com


